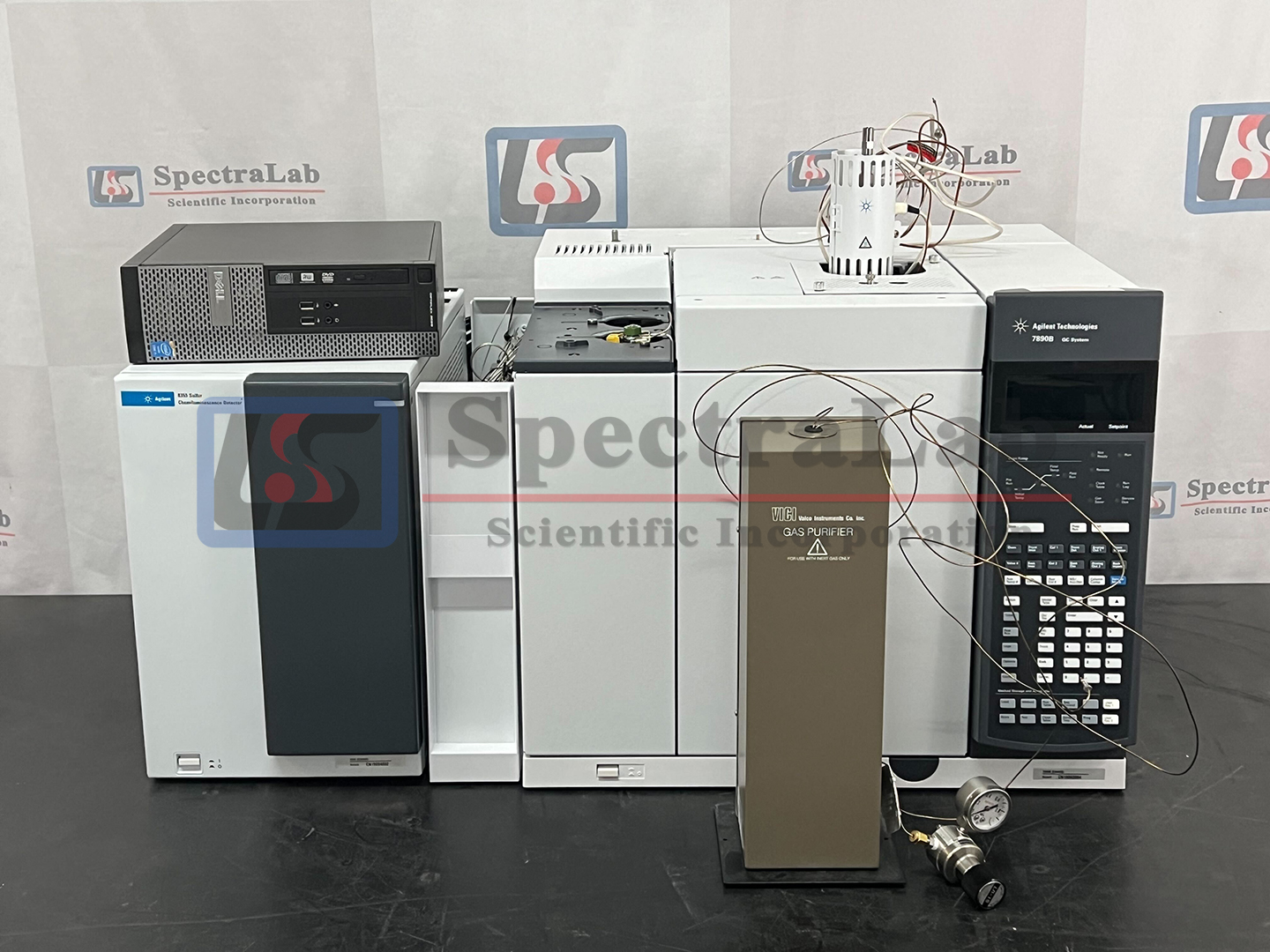
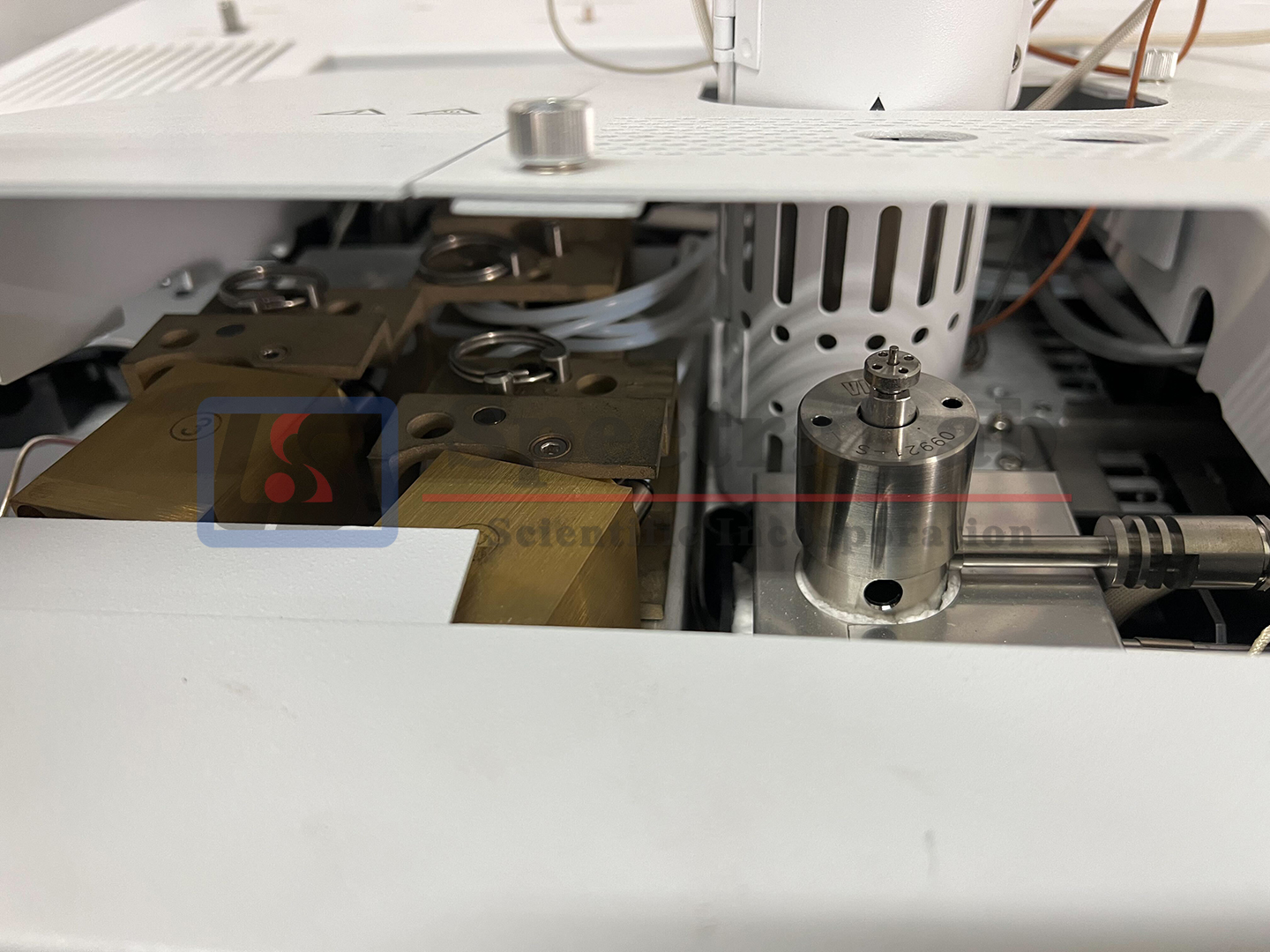
The Agilent 7890B GC is a state-of-the-art gas chromatograph that provides superior performance for all applications. Key to its performance is the use of advanced electronic pneumatic control (EPC) modules and high performance GC oven temperature control. the temperature control of the 7890B oven allows for fast and precise temperature ramping. Overall thermal performance provides optimal chromatography including peak symmetry, retention time repeatability, and retention index accuracy. The combination of precise pneumatic and temperature control leads to extremely precise retention time reproducibility, which is the basis for all chromatographic measurement.
VICI PDDs (pulsed discharge detectors) utilize a stable, low powered, pulsed DC discharge in helium as an ionization source. Eluants from the column, flowing counter to the flow of helium from the discharge zone, are ionized by photons from the helium discharge. The bias electrode(s) focus the resulting electrons toward the collector electrode, where they cause changes in the standing current which are quantified as the detector output. Performance is equal to or better than detectors with conventional radioactive sources.
In the electron capture mode, the PDD is a selective detector for monitoring high electron affinity compounds such as freons, chlorinated pesticides, and other halogen compounds. For this type of compound, the minimum detectable quantity (MDQ) is at the femtogram (10-15) or picogram (10-12) level. The PDD is similar in sensitivity and response characteristics to a conventional radioactive ECD, and can be operated at temperatures up to 400°C. For operation in this mode, He and CH4 are introduced just upstream from the column exit.
In the helium photoionization mode, the PDD is a universal, non-destructive, high sensitivity detector. The response to both inorganic and organic compounds is linear over a wide range. Response to fixed gases is positive (increase in standing current), with an MDQ in the low ppb range. The PDD in helium photoionization mode is an excellent replacement for flame ionization detectors in petrochemical or refinery environments, where the flame and use of hydrogen can be problematic. In addition, when the helium discharge gas is doped with a suitable noble gas, such as argon, krypton, or xenon (depending on the desired cutoff point), the PDD can function as a specific photoionization detector for selective determination of aliphatics, aromatics, amines, as well as other species.
The Agilent 8355 (G3489A) Sulfur Chemiluminescence Detector represents the first major advance in sulfur chemiluminescence detection in 25 years, making the technology more reliable and easier to use. Highly sensitive and highly specific, the detector is also easier to maintain, thanks to a simplified burner design with 50 percent fewer components. The most common service routine, which used to take one hour, now takes only 10 minutes. The 8355 employs a dual plasma burner to achieve high temperature combustion of sulfur-containing compounds to form sulfur monoxide (SO). A photomultiplier tube detects the light produced by the chemiluminescent reaction of SO with ozone. This results in a linear and equimolar response to the sulfur compounds, without interference from most sample matrices.
Features:
- Sulfur-specific detection for gas chromatography (GC)
- Fully integrated or standalone configurations available
- Picogram- level detection limits
- No hydrocarbon quenching
- Linear, equimolar response to sulfur compounds
- ASTM Methods compatible
- Tandem SCD and FID operation
- ~40% reduction in burner components; reduction of potential leak points
- Inner ceramic tubes replacements is a 10 minute activity